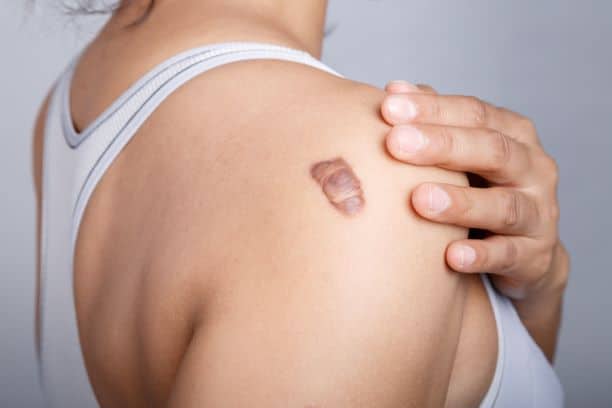
When the skin heals after an injury, it normally forms a scar to protect the wound. In some people, the healing process goes beyond what is necessary, producing a thick, raised scar that extends past the edges of the original wound. This is called a keloid, and while not dangerous, it can be a persistent and sometimes uncomfortable condition.
What Exactly Is a Keloid?
A keloid is an abnormal type of scar made up of excess collagen that continues to build long after the wound has healed. Unlike normal scars, which flatten and fade over time, keloids remain raised, firm, and often darken in color.
They can occur anywhere on the body but are most common on the chest, shoulders, back, earlobes, and jawline. Their size can vary from small, localized bumps to large, irregular growths that cover significant areas of skin.
Why Do Keloids Form?
The exact reason some people develop keloids is not completely understood, but several factors are known to increase the risk:
- Genetic predisposition – Having close relatives with keloids increases the likelihood.
- Skin type – Darker skin tones are more prone to abnormal scar formation.
- Age – Most common in people aged 10 to 30.
- Injury type – Surgical cuts, burns, piercings, acne scars, and even small scratches can trigger keloid growth.
Keloid formation is essentially the body’s healing process in overdrive—collagen production continues long after the wound has closed.
Common Symptoms
Keloids may develop weeks or even months after an injury. Symptoms include:
- Firm, raised skin over the healed wound
- Growth beyond the wound’s original borders
- Shiny, smooth texture
- Pink, red, brown, or darker coloration
- Itching or tenderness in the area
While generally harmless, they can sometimes cause discomfort or restrict movement if located over a joint.
How Are Keloids Treated?
Treating keloids can be challenging, as they have a tendency to return even after removal. However, several methods are available to reduce their size and improve their appearance.
- Steroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections are one of the most common treatments. They reduce inflammation and flatten the scar over several sessions. - Laser Therapy
Lasers help fade redness, smooth out the texture, and improve overall skin appearance. - Cryotherapy
Freezing the keloid with liquid nitrogen is effective for smaller scars. - Surgical Removal
The keloid is cut out, though recurrence rates are high unless combined with preventive measures like post-surgery steroid injections. - Silicone Gel or Sheets
Applied consistently, silicone can soften the scar and reduce its thickness. - Pressure Therapy
Compression garments apply constant pressure, restricting blood flow to the scar and slowing its growth.
Preventing Keloid Formation
If you are prone to keloids, prevention is essential. Some helpful tips include:
- Avoid unnecessary piercings or tattoos.
- Treat acne promptly to prevent deep scars.
- Use silicone sheets or gels during wound healing.
- Protect healing skin from excessive sun exposure.
- Follow your doctor’s advice closely after surgeries.
Living with Keloids
For some people, keloids are purely a cosmetic concern, while for others, they cause physical discomfort or emotional distress. The visibility of keloids—especially on the face, neck, or hands—can affect self-confidence.
Support from dermatologists, cosmetic specialists, and even counseling can help people feel more comfortable and confident. Some choose to leave keloids untreated, while others opt for active management to improve appearance and comfort.
Final Thoughts
Keloids are the result of excessive collagen production during wound healing. They can be stubborn and prone to recurrence, but with the right treatment plan, their appearance can be significantly improved. Early intervention, preventive care, and professional guidance are the keys to keeping keloids under control and maintaining healthier skin.