In industrial systems, energy efficiency is a top priority, especially when it comes to reducing operational costs and minimizing environmental impact. One of the most effective tools for improving energy efficiency is a heat exchanger. These devices are used to transfer heat between two or more fluids without them mixing. In this article, we will dive into what heat exchangers are, how they work, the different types, and how they contribute to energy savings in industrial systems.
What is a Heat Exchanger?
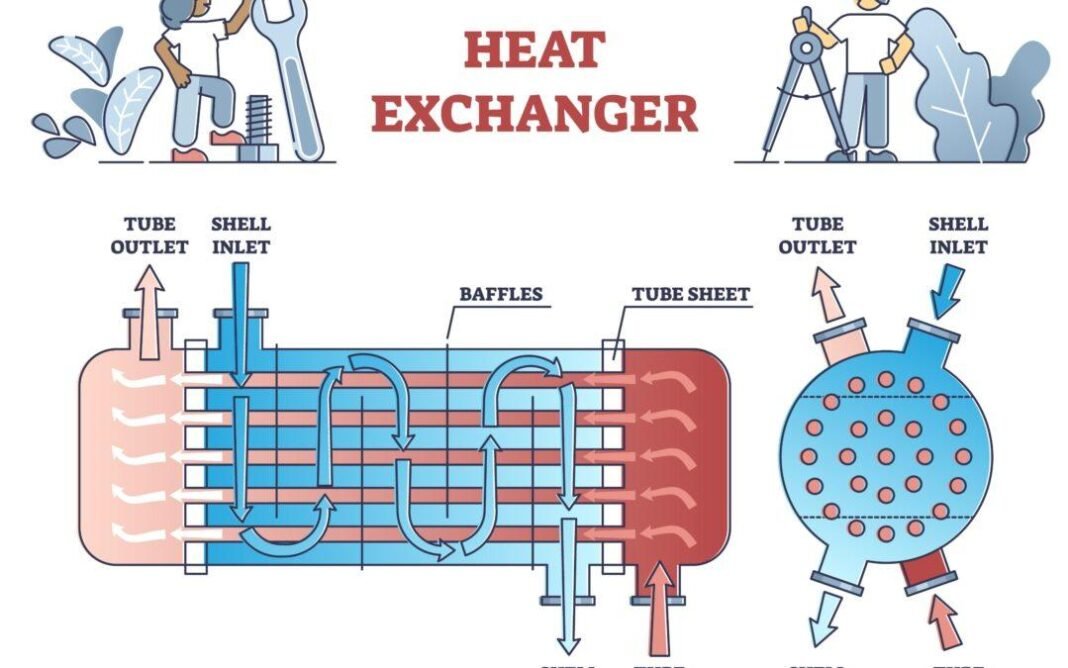
A heat exchanger is a mechanical device designed to transfer heat between two or more fluids at different temperatures. These fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing, but the heat is still transferred through the wall. Heat exchangers are widely used in applications ranging from power plants and chemical processing to HVAC systems and refrigeration. By enabling heat transfer without mixing the fluids, they can capture waste heat and reuse it, significantly improving energy efficiency.
How Heat Exchangers Improve Energy Efficiency
1. Recycling Waste Heat
In industrial systems, a significant amount of heat is often generated as a by-product of various processes. This waste heat is usually vented or released into the environment, but with a heat exchanger, this thermal energy can be recovered and repurposed. By capturing and transferring the waste heat to another fluid, a heat exchanger can reuse this energy for heating or other processes within the system. This leads to reduced fuel consumption and lower energy costs, contributing to a more sustainable operation.
2. Optimizing Thermal Management
Efficient temperature control is essential in many industrial processes, such as chemical reactions, power generation, and food processing. A heat exchanger helps maintain the optimal operating temperature by transferring heat where it is needed. For example, it can cool hot fluids in one part of the system while simultaneously warming up other fluids in another. This precise temperature management ensures processes are running at peak efficiency, preventing energy waste caused by overheating or excessive cooling.
3. Reducing the Need for Additional Heating or Cooling Systems
Without a heat exchanger, industries might rely on additional heating or cooling systems, such as boilers, cooling towers, or chillers, to regulate temperatures. These systems require significant amounts of energy to function. A well-designed heat exchanger eliminates the need for extra heating or cooling by enabling the system to naturally balance temperature differences. This reduction in the reliance on supplementary systems leads to lower energy consumption and operational costs.
4. Enhanced Heat Transfer Efficiency
Modern heat exchangers are designed to maximize heat transfer while minimizing energy loss. This is achieved through advanced materials and innovative designs that increase the surface area available for heat exchange. By improving the heat transfer efficiency, a heat exchanger ensures that the thermal energy is transferred more effectively, reducing the overall energy required to achieve the desired temperature change. The result is a more efficient system that operates with less energy input.
Types of Heat Exchangers and Their Applications
1. Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Shell and tube heat exchangers are one of the most common types used in industrial applications. These devices consist of a series of tubes, with one fluid flowing inside the tubes and another fluid flowing around the outside. They are highly effective at transferring heat between two fluids and are used in applications such as power plants, chemical processing, and oil refineries. The heat exchanger design is robust and can handle high-pressure systems, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial use.
2. Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers are made up of multiple thin, corrugated plates that are stacked together to create channels for fluid flow. This type of heat exchanger is known for its compact design and high heat transfer efficiency. Plate heat exchangers are commonly used in industries such as food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, and HVAC systems. Their efficient use of space and energy makes them an excellent choice for systems with limited space or lower flow rates.
3. Air Cooled Heat Exchangers
Air cooled heat exchangers use ambient air to cool the fluids inside the system. These heat exchangers are particularly useful in areas where water is scarce or when cooling needs to be achieved without relying on water-based systems. Air cooled heat exchangers are often found in petrochemical plants, gas turbines, and HVAC systems. They are an energy-efficient option for cooling, especially in areas with high temperatures or where water conservation is essential.
4. Double Pipe Heat Exchangers
Double pipe heat exchangers consist of two concentric pipes, with one fluid flowing inside the inner pipe and the other flowing in the outer pipe. This simple design is highly effective in smaller systems or applications where the heat exchange process doesn’t require a complex arrangement of tubes. These heat exchangers are typically used in smaller-scale industrial systems or laboratory applications.
Key Industries That Benefit from Heat Exchangers
1. Chemical and Petrochemical Industry
Heat exchangers are essential in chemical processing plants for controlling temperatures during various reactions and for condensing or evaporating fluids. By recovering waste heat, these devices improve energy efficiency, reduce costs, and help meet sustainability goals. For example, heat exchangers can be used to transfer heat from an exothermic reaction to an endothermic reaction, optimizing the overall energy balance of the process.
2. HVAC Systems
In the HVAC industry, heat exchangers play a critical role in improving energy efficiency in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. These devices ensure that heat is transferred efficiently within buildings, keeping indoor temperatures regulated while minimizing energy use. By recovering waste heat from exhaust air and transferring it to incoming fresh air, heat exchangers can help buildings maintain a comfortable climate with less energy input.
3. Power Generation
Power plants rely on heat exchangers to transfer thermal energy between fluids, making them a critical component of power generation. In these systems, heat exchangers are used to cool down hot gases, condense steam, and optimize the heat recovery process. By improving the overall efficiency of power generation, these devices help reduce fuel consumption and minimize environmental impact.
4. Food and Beverage Industry
Heat exchangers are widely used in the food and beverage industry for pasteurization, cooling, and heating processes. They enable the industry to maintain product safety and quality while improving energy efficiency. Whether in dairy, brewing, or juice production, heat exchangers help ensure that products are processed at the optimal temperature with minimal energy waste.
Conclusion: The Role of Heat Exchangers in Sustainable Industrial Practices
In conclusion, heat exchangers are essential devices in improving energy efficiency across various industrial sectors. Whether they are used to recycle waste heat, optimize thermal management, or reduce the need for additional heating or cooling systems, heat exchangers play a pivotal role in minimizing energy consumption and operational costs. By adopting these technologies, industries can achieve greater sustainability, improve profitability, and reduce their carbon footprint, paving the way for a more energy-efficient future in industrial operations.